-

北师大初中数学八年级上册平行线的性质1教案
方法总结:平行线与角的大小关系、直线的位置关系是紧密联系在一起的.由两直线平行的位置关系得到两个相关角的数量关系,从而得到相应角的度数.探究点四:平行于同一条直线的两直线平行如图所示,AB∥CD.求证:∠B+∠BED+∠D=360°.解析:证明本题的关键是如何使平行线与要证的角发生联系,显然需作出辅助线,沟通已知和结论.已知AB∥CD,但没有一条直线既与AB相交,又与CD相交,所以需要作辅助线构造同位角、内错角或同旁内角,但是又要保证原有条件和结论的完整性,所以需要过点E作AB的平行线.证明:如图所示,过点E作EF∥AB,则有∠B+∠BEF=180°(两直线平行,同旁内角互补).又∵AB∥CD(已知),∴EF∥CD(如果两条直线都和第三条直线平行,那么这两条直线也互相平行),∴∠FED+∠D=180°(两直线平行,同旁内角互补).∴∠B+∠BEF+∠FED+∠D=180°+180°(等式的性质),即∠B+∠BED+∠D=360°.方法总结:过一点作一条直线或线段的平行线是我们常作的辅助线.

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册I’m going to be a basketball player教案3篇
教学目标1.知识目标:(1)学习What are you going to be when you grow up?/How are you going to do that?句式。(2)学会用英语描述有关职业的表达法。2.能力目标:(1)能够谈论为实现理想所做出的打算和安排。(2)能够谈论未来自己与他人理想的职业及原因。(3)能用英语描述课余时间的活动安排,最终具备表达综合信息的能力。3.情感目标:新学期到来之际,让他们在学习、体育、饮食、特长、读书等方面制定计划,教育学生合理安排自己的课外生活,思考自己的理想职业及适合自己的职业。教学重点、难点本单元的重点为“be going to”表将来,want to be, what,where, when,how引导的特殊疑问句。难点是语言目标的实现。教材分析本单元以I am going to be a basketball player为话题,共设计了三部分的内容:一、Section A该部分有4个模块。第一模块围绕Do you think these jobs are interesting?这一话题展开思维(1a)、听力(1b)、口语(1c)训练;

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册How was your school trip教案2篇
“Go for it!” is based on “Task-Based Language Teaching”. It adheres to “The authenticity principle”, “The form-function principle”, “The task dependency principle” and “The principle of learning by doing”. These principles all accord with the demands of curriculum focus.In and of Grade Seven (II), “Go for it!”, students have learned “The Simple Past Tense”. And it appears again in of Grade Eight (I). teaches students more about how to talk about events in the past. In addition, it gives affirmative and negative statements in the past tense, such as the sentence patterns “Did you see …?” “Were there …?” “Did you go …?” As the first part of Unit 8, Section A opens with a picture presenting the last school trip in the aquarium and continues with several step-by-step practice activities, which are all good for students to master “The Simple Past Tense”. Doing well in Section A will help students integrate the new target language with that in Section B. Thus, they can describe the events in the past freely and foster their own ability of reflecting and practicing. II. Teaching ObjectivesTeaching objective is the beginning and aim of teaching activities. According to the overall goal of the English elementary course--- improve students' synthetic ability of language application, which should be based on the development of students’ “Language knowledge”, “Language skills”, “Character building”, “Learning strategies” and “Cross-cultural awareness”. The teaching objectives are described as follows(I). Knowledge objectivesi. Master the simple past tense of regular and irregular verbsii. Recite the new words and expressions about the last school trip in the aquarium, including their pronunciation and intonation

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册Could you please clean your room教案3篇
一、 教学内容Section A 1a----1c二、 教学目标1.学习词汇do the dishes, make the bed, take out the trash, fold the clothes, do the laundry, sweep the floor, clean the living room.2.句型 Could you please clean your room? Yes, sure.三、 教学准备 学生预习本单元所有的词汇多媒体课件 活动表 奖品四、 教学过程Pre-task1. Warming upEnjoy ourselves. Watch cartoon Cinderella. 看动画片段《灰姑娘》导如入本课话题和新词汇“chores”美丽善良的鬼姑娘因继母的嫉妒,每天得做所有的家务。片段的主题使学生联想到本课的话题。2. learn new words and phrasesLook! What is she / he dong? 看图学习动词词组do chores, do the dishes, make the bed, take out the trash, fold the clothes, do the laundry, clean the living room.3. Guessing game.What is she doing ? 4. Pair work. 1a, Do you do these things at home? Write “Y” for “yes” and “N” for “no”.5. Listening . 1b , Peter’s chores or Mom’s chores?理解目标语Could you please clean your room? Yes, sure.Write “M” for Mom’s chores, “P” for Peter’s chores in the chart.6. PairworkLook at the picture,Ask your partner to do the chores that you see. 7. Interview Who is the most able at home? 1) What chores do you do at home? How often do you do the chores? Work in four, interview each of the students in the group, fill in the chart.

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册How do you get to school教案2篇
Step Ⅶ Role play ( Work on 1b)1. First ask two students to read the dialogue to the class.Sa: How do you get to school?Sb: Well, I ride my bike to the subway station. Then I take the subway.2. Now work with a partner.Suppose you use two kinds of transportation to get to school \Hangzhou\Beijing... (bus, train, subway, walking, bike, etc.) Tell how you get there. You may use the phrases in 1a.3. Then ask different pairs of students to present their conversations to the class.Step ⅧListening1. Work on 2a(1) First ask students to read the list of information that Thomas wants to know.…where Nina lives.…how far from school she lives.…how long it takes to get to school.…how she gets to school.…what she thinks of the transportation.(2) Tell students what transportation and bus stop mean.bus stop 汽车站 transportation n. 运送;运输Then tell students we'll hear a recording. Please put a checkmark in front of each thing that Thomas wants to know.(3) Now play the recording for students.( Have students pay attention to the sample answer.) (4) Then correct the answers.

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册What are you doing for vacation教案2篇
Teaching goals : 1. Words & phrases: babysit ,get back , fishing , rent , think about , decide(on) , tourist etc. 2. How to talk about future plans . 3. 现在进行时表示将来计划或行动. 4. 特殊疑问句(where , when , how long引导) Important and difficult points : Drills :What are you doing for vacation ? I’m watching TV . When are you going ? I’m going … . How long are you staying ? We’re staying for five days . Teaching aids : cards and a tape ,a large wall calendar . Period 1 Teaching procedures : Step 1Leading in1. Free talk . 2. Put up the wall calendar . T: I’m staying home on Saturday (pointing to next Saturday ).Ss repeat . Ss: I’m staying home on Saturday . T: OK. Today we’ll learn how to talk about future plans. Step 2Pre-task SB Page 13 , 1a . 1. Look at the picture carefully and tell what you see in the picture . 2. Write the activities from the pictures in the box and add some more . 3. Practice reading . Step 3While-task1. Using the activities we write in 1a to make conversations .For example :What are you doing for vacation ? I’m visiting my uncle . 2. Pairwork .Practice in pairs . 3. 用第三人称练习对话.

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册I’m more outgoing than my sister教案2篇
1 交通工具的比较此活动为小组活动。学生通过讨论找出到达某一城市可乘坐的各种交通工具,并选择最佳出行方式。Teacher:We’re going to Shanghai. How many ways can we use to get there? Yes, there are four ways: by bus, by plane, by train, by ship. Please discuss how you are going to get there.操作建议:(1)学生以小组为单位展开活动,谈论本组所选择的交通工具。(2)各组选代表向全班汇报,阐述本组所选择的交通工具的利和弊。完成任务所需要的语言结构:We can go there by ship. It’s more comfortable and cheaper than any other transportation.We can go there by bus. It’s cheaper but it takes longer time.2 哪个城市更合适?此活动具有挑战性。假设中国要举行2014年世界杯足球赛,分别从历史,人文,天气等方面对各城市(北京,大连,上海,昆明)进行比较,选择最佳举办城市。T: Imagine China is holding the 2014 FIFA World Cup. Which city do you think is the best for the World Cup, Beijing, Dalian, Shanghai or Kunming? Let’s work in groups. If you choose Beijing, please join the Team Red. If you chose Dalian, please join the Team White. If you choose Shanghai, please join the Team Blue. If you choose Kunming, please join the Team Green. Please show us its advantages. Then let’s see which team will win.

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册What’s the best radio station教案2篇
教学重点和难点:运用所掌握的语言描述,比较不同地点的特点。在练习中学习掌握英语比较级和最高级的用法。课前准备分配小组,每组五至六人。通过上网或翻阅报刊杂志等方法,确定旅游线路,做出基本的旅游计划。教学设计:本节课流程图 学法指导:1.由于这是一堂新课,在教学中应注意面向全体,发挥学生的主体性,引导学生积极参与,激发学生的求知欲和学习积极性,指导学生积极思维,主动获取知识,养成良好的学习方法。逐步学会独立解决问题。总之要尽可能调动学生的非智力因素促进智力因素的发展。教法选择:1.电化教学法2.课堂讨论法3.任务型教学法采用这些方法的目的是为了充分调动学生的学习积极性,使学生变被动学习为主动学习。通过电脑形象的演示,加强印象,提高兴趣,突破难点,提高教学效率,进而增大教学的容量和信息量。充分体现教师为主导,学生为主体的教学原则。

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册What’s the matter教案2篇
She shouldn’t go to the party tonight.Step7. TaskT: You know, there are lots of problems in our life. If you are a doctor, please tell us how to solve the problem. I will divide you into 9 groups. Please work in groups. And then choose one of you to report your ideas.The following are the problems:I have a toothache.I am hungry. I have a sore throat.I am stressed out. I have a sore back.I am tired. I can’t sleep.I have a cold. I have a headache.Report: If you have a headache, you should go to bed early. You should see the doctor. You should eat some medicine. You shouldn’t wash your face with cold water.You shouldn’t sleep late.You shouldn’t swim.…..T encourages the students to give advice as much as possible.Homework:1. Chose one of the problems, and write down your advice2. Copy the new words这一步是用于热身的,同时也可以让他们复习一部分的表示人体部位的单词,扩充知识.学习语言的过程也是一个不断积累的过程,复习旧知识,增添新知识.通过小游戏,强化学生对Does she/he have…这个句子的运用能力.通过复习,自然的引到下面新知识的学习。充分利用表格,由句子到对话,再到文章,让学生循序渐进. 提高学生的综合语言运用能力,运用以前学过的知识来解决身边的问题.Period 5 (Section B 3a—3c, selfcheck)教学内容与分析:

人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册Can you come to my party教案3篇
Step 3 (3b)First, tell the students when we talk about our future plans, we often use: I’m+verb+ing When we talk about what we must do, we use have to. Ask the students to fill in the blanks in 3b. The answers are: shopping, go to see, a test, I’m going, my family. Step 4 (3c)Let the students write an e-mail message to a friend. Say why you can’t visit next. Before the exercise, ask the students to give some possible answers and write them on the blackboard. So the students will feel easy to finish the writing exercise. After they finish it, Let them to correct it in groups first. Each group chooses theirs best one to read in front of the whole class. Step 5 ( planning a party )First read the conversation in the box together. Then ask the students to turn to page 88.Write down everything you have to do next week. Write in all the things you have to do . Ask the students to look at the list. Ask them “What day are you free?” This is when you can have your party. Step 6 (Self check 1 )Let the students to fill in the blanks with the words given. Change the forms of the words if possible. Then make their own sentences. The answers are: visit, playing, have to, study, comeStep 7 (Self check 2)Imagine you are Marie. Read the information and look at your schedule. Write replies to the invitation.
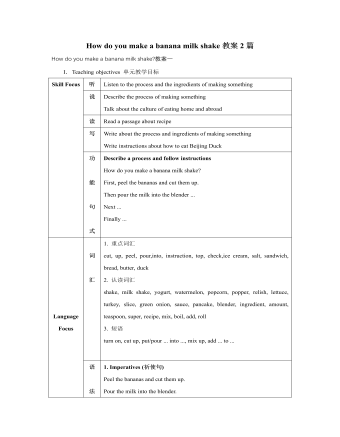
人教版新目标初中英语八年级上册How do you make a banana milk shake教案2篇
1. First, ... then, ... next, ... finally, ...首先,……然后,……接着,……最后,……这是英语中表达做某事的步骤的一种说法。如果步骤较多,还可以说:first-next-after that-later on-finally/at last通常你会听到说英语国家的人在说 first, next, then, finally 和后面的内容时,他们会做一些停顿。这样就能提前告诉听者接下来讲的是一系列的步骤。这一点在朗读和听力中应特别注意。2. how many, how much均为疑问词,同是“多少”,但用法不同。请看:how many修饰可数名词复数,how much修饰不可数名词。但在用法上,同学们常犯如下错误:1) [误] How many are there bananas on the table?[正] How many bananas are there on the table?[析] how many, how much 中的many,much是形容词,常修饰名词作定语,故后面跟名词。2) [误]How much tea are there on the table?[正]How much tea is there on the table?[析] how much修饰不可数名词时,谓语动词用单数。how many与how much的区别可简记为:前how many:问“多少”,复数名词后面跑;how much问“多少”,不可数名词单数好。前者答语用基数词,后者答语用数量关系。

北师大初中数学八年级上册估算2教案
在探究估算方法的时候,教师要注重适时的引导,以免让学生无从下手.在教学过程中一定要让学生体会估算的实用价值,了解到“数学既来源与生活,又回归到生活为生活服务”.(二)课堂评价的一些思考在教学中要多鼓励学生用自己的语言表达他们的想法,在估算的过程中多给予适当的引导和评价,让学生逐步把握估算的方法,找到解决问题的信心.比如对“画能挂上去吗”这个问题情境,学生可能提出不同的看法,有些学生可能认为可以挂上去,因为人还有身高,完全可以弥补梯子稳定摆放的高度和挂画位置的高度之间的差距,有些学生可能认为,人不可能爬到梯子的顶部,加上人如果本来比较矮,画就不能挂上去等等想法,教师都应该给予肯定,这样才能激发学生思考问题的热情,调动学生探究问题的积极性.作为教师,一定要尊重学生的个体差异,满足多样化的学习需要,鼓励探究方式、表达方式和解题方法的多样化.

北师大初中数学八年级上册定义与命题2教案
② 命题的含义:判断一件事情的句子,叫做命题,如果一个句子没有对某一件事情作出任何判断,那么它就不是命题.活动目的:通过课后的总结,使学生对定义、命题等概念有更清楚的认识,让学生在头脑中对本节课进行系统的归纳与整理.教学效果:学生在有了前面对定义、特别是命题概念的学习后,能了解命题的结构,以及哪些是命题,使学生对命题的学习有了清楚的认识。第五环节 课后练习学习小组搜集八年级数学课本中的新学的部分定义、命题,看谁找得多.四、教学反思本节课的设计具有如下特点:(1)采用了“小品表演”的形式引入新课,意在激起学生对数学的兴趣,让学生知道,数学不是枯燥无味的。并能从表演中不同的人对“黑客”这个名词的不同理解更好地悟出“定义”的含义。

北师大初中数学八年级上册定理与证明2教案
第一环节:回顾引入活动内容:①什么叫做定义?举例说明.②什么叫命题?举例说明. 活动目的:回顾上节知识,为本节课的展开打好基础.教学效果:学生举手发言,提问个别学生.第二环节:探索命题的结构活动内容:① 探讨命题的结构特征观察下列命题,发现它们的结构有什么共同特征?(1)如果两个三角形的三条边对应相等,那么这两个三角形全等.(2)如果一个三角形是等腰三角形,那么这个三角形的两个底角相等.(3)如果一个四边形的一组对边平行且相等,那么这个四边形是平行四边形.(4)如果一个四边的对角线相等,那么这个四边形是矩形.(5)如果一个四边形的两条对角线互相垂直,那么这个四边形是菱形.② 总结命题的结构特征(1)上述命题都是“如果……,那么……”的形式.(2)“如果……”是已知的事项,“那么……”是由已知事项推断出的结论.

北师大初中数学八年级上册代入法1教案
【类型三】 已知方程组的解,用代入法求待定系数的值 已知x=2,y=1是二元一次方程组ax+by=7,ax-by=1的解,则a-b的值为()A.1 B.-1 C.2 D.3解析:把解代入原方程组得2a+b=7,2a-b=1,解得a=2,b=3,所以a-b=-1.故选B.方法总结:解这类题就是根据方程组解的定义求,即将解代入方程组,得到关于字母系数的方程组,解方程组即可.三、板书设计解二元一,次方程组)基本思路是“消元”代入法解二元一次方程组的一般步骤回顾一元一次方程的解法,借此探索二元一次方程组的解法,使得学生的探究有很好的认知基础,探究显得十分自然流畅.充分体现了转化与化归思想.引导学生充分思考和体验转化与化归思想,增强学生的观察归纳能力,提高学生的学习能力.

北师大初中数学八年级上册定义与命题1教案
一、情境导入神舟十号是中国神舟号系列飞船之一,主要由推进舱(服务舱)、返回舱、轨道舱组成.神舟十号在酒泉卫星发射中心“921工位”,于2013年6月11日17时38分02.666秒发射,由长征二号F改进型运载火箭(遥十)“神箭”成功发射.在轨飞行十五天左右,加上发射与返回,其中停留天宫一号十二天,共搭载三位航天员——聂海胜、张晓光、王亚平.6月13日与天宫一号进行对接.6月26日回归地球.要读懂这段报导,你认为要知道哪些名称和术语的含义?二、合作探究探究点一:定义 下列语句属于定义的是()A.明天是晴天B.长方形的四个角都是直角C.等角的补角相等D.平行四边形是两组对边分别平行的四边形解析:作出正确选择的关键是理解定义的含义.A是对天气的预测,B是描述长方形的性质,C是描述补角的性质.只有D符合定义的概念.故选D.方法总结:定义指的是对术语和名称的含义的描述,是对一个事物区分于其他事物的本质特征的描述,而不是对其性质的判断.

北师大初中数学八年级上册定理与证明1教案
求证:直角三角形的两个锐角互余.解析:分析这个命题的条件和结论,根据已知条件和结论画出图形,写出已知、求证,并写出证明过程.已知:如图所示,在△ABC中,∠C=90°.求证:∠A与∠B互余.证明:∵∠A+∠B+∠C=180°(三角形内角和等于180°),又∠C=90°,∴∠A+∠B=180°-∠C=90°.∴∠A与∠B互余.方法总结:解此类题首先根据题意将文字语言变成符号语言,画出图形,最后再经过分析论证,并写出证明的过程.三、板书设计命题分类公理:公认的真命题定理:经过证明的真命题证明:推理的过程经历实际情境,初步体会公理化思想和方法,了解本教材所采用的公理,让学生对真假命题有一个清楚的认识,从而进一步了解定理、公理的概念.培养学生的语言表达能力.

北师大初中数学八年级上册加减法1教案
已知xm-n+1y与-2xn-1y3m-2n-5是同类项,求m和n的值.解析:根据同类项的概念,可列出含字母m和n的方程组,从而求出m和n.解:因为xm-n+1y与-2xn-1y3m-2n-5是同类项,所以m-n+1=n-1,①3m-2n-5=1.②整理,得m-2n+2=0,③3m-2n-6=0.④④-③,得2m=8,所以m=4.把m=4代入③,得2n=6,所以n=3.所以当m=4,n=3时,xm-n+1y与-2xn-1y3m-2n-5是同类项.方法总结:解这类题,就是根据同类项的定义,利用相同字母的指数分别相等,列方程组求字母的值.三、板书设计用加减法解二元一次方程组的步骤:①变形,使某个未知数的系数绝对值相等;②加减消元;③解一元一次方程;④求另一个未知数的值,得方程组的解.进一步理解二元一次方程组的“消元”思想,初步体会数学研究中“化未知为已知”的化归思想.选择恰当的方法解二元一次方程组,培养学生的观察、分析问题的能力.

北师大初中数学八年级上册确定位置1教案
解析:要在地球仪上确定南昌市的位置,需要知道它的经纬度,故选D.方法总结:本题考查了坐标确定位置,熟记位置的确定需要横向与纵向的两个数据是解题的关键.【类型二】 用“区域定位法”确定位置如图所示是某市区的部分简图,文化宫在D2区,体育场在C4区,据此说明医院在________区,阳光中学在________区.解析:本题首先给出的是表示文化宫和体育场的位置,即D2区和C4区,这就确定了本题中表示建筑物位置的方法,即字母表示列数,数字表示行数.故填A3,D5.方法总结:解此类题先要弄清区域定位法中字母及数字各自表示的含义,再用已知的表示方法来确定相关位置.三、板书设计确定位置有序实数对方位法经纬度区域定位法将现实生活中常用的定位方法呈现给学生,进一步丰富学生的数学活动经验,培养学生观察、分析、归纳、概括的能力.教学过程中创设生动活泼、直观形象、且贴近他们生活的问题情境;另一方面,为学生创造自主学习、合作交流的机会,促使他们主动参与、积极探究.

北师大初中数学八年级上册认识无理数2教案
本节课中教师首先用拼图游戏引发学生学习的欲望,把课程内容通过学生的生活经验呈现出来,然后进行大胆置疑,生活中的数并不都是有理数,那它们究竟是什么数呢?从而引发了学生的好奇心,为获取新知,创设了积极的氛围.在教学中,不要盲目的抢时间,让学生能够充分的思考与操作.(二)化抽象为具体常言道:“数学是锻炼思维的体操”,数学教师应通过一系列数学活动开启学生的思维,因此对新数的学习不能仅仅停留于感性认识,还应要求学生充分理解,并能用恰当数学语言进行解释.正是基于这个原因,在教学过程中,刻意安排了一些环节,加深对新数的理解,充分感受新数的客观存在,让学生觉得新数并不抽象.(三)强化知识间联系,注意纠错既然称之为“新数”,那它当然不是有理数,亦即不是整数,也不是分数,所以“新数”不可以用分数来表示,这为进一步学习“新数”,即第二课时教学埋下了伏笔,在教学中,要着重强调这一点:“新数”不能表示成分数,为无理数的教学奠好基.





















