-

新人教版高中英语必修3Unit 5 The value of money-Reading and Thinking教学设计二
? Could you offer me some kind of work here?? I don’t want your charity, I just want an honest job.? Careless: I landed in Britain by accident.Step 7:Consolidation.? Find Henry? Roderick and Oliver were I .making a bet when they saw Henry, a poor young man. ? Know Henry? About a month ago, Henry was sailing and later he found himself carried out to sea by a strong wind. Fortunately, he 2.was spotted by a ship. And it was the ship that brought him to 3.England? Offer money to Henry ? Oliver and Roderick gave Henry a letter and told him that there was money in it. They 4.persuaded him to accept it, and made him 5.promise that it wouldn't be opened until 2 o'clock.Step 8:Language pointsa large amount of: a large quantity of; a great deal ofe.g. They bought a large amount of furniture before they moved their new house.make a bet: make an arrangement to risk money, etc. on an event of which the result is doubtful.e.g. We made a bet on the result of the match.permit sb to do something: allow somebody to do somethinge.g. My mother doesn’t permit me to ride in the street after it rained.by accident: as a result of chancee.g. I only found it by accident.stare at: look at somebody or something with the eyes wide open in a fixed gaze( in astonishment, wonder, fear, etc)to be honest: to tell you the truth; to be franke.g. To be honest, I don’t think we have a chance of winning.Step7 Homework:What do you think will happen to Henry? Will the bank-note help him or get him into trouble?

新人教版高中英语必修3Unit 5 The Value of Money-Reading and Thinking教学设计一
Everybody wants to get wealth.In today’s material world,making money or becoming wealthy symbolizes a person’s success and capability. Many people just make every effort, pay any price to attain greater wealth. With money,they can buy nice, large apartments in nice neighborhood. With money they can own luxurious cars. Wealth seems to bring all happiness in life.But is wealth the only road to happiness? Not really. There are many things in the world, which are beyond the means of money, such as friendship, love, health and knowledge. People are so preoccupied with struggling for money that they have no time or would not take the time to form or maintain friendship. What happiness can they feel living as lonely miserable creatures without love or friends in the world even if they accumulate tremendous wealth?In my opinion, people can’t do anything without money, but money is not everything. What money will bring you depends on your personal belief and goal in life. If you are kind enough to help others, especially the poor, money is a good thing to you. With it, you can do much more for the benefit of people and your country, and it will add to your own happiness. If you want money just for your own needs, you’ll never be satisfied or happy. In a word,you should have money spent for more people. Only then can money be the source of your happiness.Step 8 Homework4 students in a group, one acts Roderick, one Oliver, one servant and the fourth one acts Henry Adams, then listen to the tape, pay more attention to the difference between American English and British English in pronunciation, stress, tone.

新人教版高中英语必修3Unit 5 The Value of Money-Reading for Writing教学设计二
2. 您能看到, 我头发太长了。You can see that my hair is much too long.3. 无论什么时候, 只要您想回来就回来。Please come back whenever you want.4. 您仅有很少的头发要理! You only have too little hair to cut !5. 为您服务是我的荣幸!It is my honour to serve you!Step 9 Writing(Henry is walking down the street when he sees a sign for a place that cuts hair. He decides to have it cut. )H=Henry B=BarberH: Good afternoon, I’d like to have my hair cut, if I may. (The barber looks at Henry’s hair and continues cutting another man’s hair. ) Er, I’d really like a haircut. As you can see it’s much too long. B: (in a rude manner) Yes, I can see that. Indeed, I can. H: Fine, well, I’ll have a seat then. (He sits in one of the barber’s chairs. The barber turns to look at Henry. )B: It’s quite expensive here, you know! Are you sure you can afford it?H: Yes. I think so. (After his hair is cut, the barber tells Henry how much he must pay. Henry shows the barber the bank note. )B: Why Mr. . . (looks shocked)H: Adams. Henry Adams. I’m sorry. I don’t have any change. B: Please don’t worry! (wearing a big smile) Nothing to worry about! Nothing at all! Please come back whenever you want, even if you only have too little hair to cut! It will be my honour to serve you!Step 10 Pair workExchange drafts with a partner. Use this checklist to help your partner revise his/her draft.1. Are all the elements of a play included and in good order ?2. Do the character use suitable language ?3. Are the stage directions clear and useful ?4. Is the plot clear and exciting enough ?

新人教版高中英语必修3Unit 5 the value of money-Reading For Writing教学设计一
【参考范文】Narrator:(Henry is smiling as he leaves the restaurant. As he is walking down the street, he sees a sign for a place that cuts hair. He decides to get it cut. )H=Henry;B=Barber;R=rude manH:Good afternoon, I'd like to get a cut, if I may. (The barber looks at Henry's hair and continues cutting another man's hair. )Er, I'd really like a haircut. As you can see it's much too long. B:(in a rude manner) Yes, I can see that. Indeed, I can. H:Fine, well I'll have a seat then. (He sits in one of the barber's chairs. The barber turns to look at Henry. )B:It's quite expensive here, you know!Are you sure you can afford it?H:Yes. I think so. (In comes the rude man. )R:Hey you there. I need a haircut quickly. Can you do me straightaway?B:All right, then, get in the chair and I'll see what I can do. R:Thank you. (sits down in one of the barber's chairs)H:Excuse me, but I was here first. Aren't you going to do my hair first?B:This man's in a hurry. H:Well so am I!I insist that you cut my hair first. B:OK, but I'll have to be quick. This gentleman is waiting. H:Thank you. (They both become quiet. After his hair is cut, the barber tells Henry how much he must pay. Henry shows the barber the bank note. )B:Why, Mr . . . (looks shocked)H:Adams. Henry Adams. I'm sorry, I don't have any change. R:You're that Mr Adams! Well,I'm glad I waited or I might never have known it was you. B:Why, Mr Adams, please don't worry!(wearing a big smile) Nothing to worry about!Nothing at all!Please come back any time, even if you only need too little hairs cut!It will be my honour to serve you!

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Discovering useful structures教学设计
The grammatical structure of this unit is predicative clause. Like object clause and subject clause, predicative clause is one of Nominal Clauses. The leading words of predicative clauses are that, what, how, what, where, as if, because, etc.The design of teaching activities aims to guide students to perceive the structural features of predicative clauses and think about their ideographic functions. Beyond that, students should be guided to use this grammar in the context apporpriately and flexibly.1. Enable the Ss to master the usage of the predicative clauses in this unit.2. Enable the Ss to use the predicative patterns flexibly.3. Train the Ss to apply some skills by doing the relevant exercises.1.Guide students to perceive the structural features of predicative clauses and think about their ideographic functions.2.Strengthen students' ability of using predicative clauses in context, but also cultivate their ability of text analysis and logical reasoning competence.Step1: Underline all the examples in the reading passage, where noun clauses are used as the predicative. Then state their meaning and functions.1) One theory was that bad air caused the disease.2) Another theory was that cholera was caused by an infection from germs in food or water.3) The truth was that the water from the Broad Street had been infected by waste.Sum up the rules of grammar:1. 以上黑体部分在句中作表语。2. 句1、2、3中的that在从句中不作成分,只起连接作用。 Step2: Review the basic components of predicative clauses1.Definition

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 4 Journey Across a Vast Land教学设计
当孩子们由父母陪同时,他们才被允许进入这个运动场。3.过去分词(短语)作状语时的几种特殊情况(1)过去分词(短语)在句中作时间、条件、原因、让步状语时,相当于对应的时间、条件、原因及让步状语从句。Seen from the top of the mountain (=When it is seen from the top of the mountain), the whole town looks more beautiful.从山顶上看,整个城市看起来更美了。Given ten more minutes (=If we are given ten more minutes), we will finish the work perfectly.如果多给十分钟,我们会完美地完成这项工作。Greatly touched by his words (=Because she was greatly touched by his words), she was full of tears.由于被他的话深深地感动,她满眼泪花。Warned of the storm (=Though they were warned of the storm), the farmers were still working on the farm.尽管被警告了风暴的到来,但农民们仍在农场干活。(2)过去分词(短语)在句中作伴随、方式等状语时,可改为句子的并列谓语或改为并列分句。The teacher came into the room, followed by two students (=and was followed by two students).后面跟着两个学生,老师走进了房间。He spent the whole afternoon, accompanied by his mom(=and was accompanied by his mom).他由母亲陪着度过了一整个下午。

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Learning about Language教学设计
Step 7: complete the discourse according to the grammar rules.Cholera used to be one of the most 1.__________ (fear) diseases in the world. In the early 19th century, _2_________ an outbreak of cholera hit Europe, millions of people died. But neither its cause, 3__________ its cure was understood. A British doctor, John Snow, wanted to solve the problem and he knew that cholera would not be controlled _4_________ its cause was found. In general, there were two contradictory theories 5 __________ explained how cholera spread. The first suggested that bad air caused the disease. The second was that cholera was caused by an _6_________(infect) from germs in food or water. John Snow thought that the second theory was correct but he needed proof. So when another outbreak of cholera hit London in 1854, he began to investigate. Later, with all the evidence he _7_________ (gather), John Snow was able to announce that the pump water carried cholera germs. Therefore, he had the handle of the pump _8_________ (remove) so that it couldn't be used. Through his intervention,the disease was stopped in its tracks. What is more, John Snow found that some companies sold water from the River Thames that __9__________________ (pollute) by raw waste. The people who drank this water were much more likely _10_________ (get) cholera than those who drank pure or boiled water. Through John Snow's efforts, the _11_________ (threaten) of cholera around the world saw a substantial increase. Keys: 1.feared 2.when 3. nor 4.unless 5.that/which 6.infection 7.had gathered 8.removed 9.was polluted 10.to get 11. threat

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Reading and thinking教学设计
Step 5: After learning the text, discuss with your peers about the following questions:1.John Snow believed Idea 2 was right. How did he finally prove it?2. Do you think John Snow would have solved this problem without the map?3. Cholera is a 19th century disease. What disease do you think is similar to cholera today?SARS and Covid-19 because they are both deadly and fatally infectious, have an unknown cause and need serious public health care to solve them urgently.keys:1. John Snow finally proved his idea because he found an outbreak that was clearly related to cholera, collected information and was able to tie cases outside the area to the polluted water.2. No. The map helped John Snow organize his ideas. He was able to identify those households that had had many deaths and check their water-drinking habits. He identified those houses that had had no deaths and surveyed their drinking habits. The evidence clearly pointed to the polluted water being the cause.3. SARS and Covid-19 because they are both deadly and fatally infectious, have an unknown cause and need serious public health care to solve them urgently.Step 6: Consolidate what you have learned by filling in the blanks:John Snow was a well-known _1___ in London in the _2__ century. He wanted to find the _3_____ of cholera in order to help people ___4_____ it. In 1854 when a cholera __5__ London, he began to gather information. He ___6__ on a map ___7___ all the dead people had lived and he found that many people who had ___8____ (drink) the dirty water from the __9____ died. So he decided that the polluted water ___10____ cholera. He suggested that the ___11__ of all water supplies should be _12______ and new methods of dealing with ____13___ water be found. Finally, “King Cholera” was __14_____.Keys: 1. doctor 2. 19th 3.cause 4.infected with 5.hit 6.marked 7.where 8.drunk 9.pump 10.carried 11.source 12.examined 13.polluted 14.defeatedHomework: Retell the text after class and preview its language points

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 2 Bridging Cultures-Discovering useful structures教学设计
The grammar of this unit is designed to review noun clauses. Sentences that use nouns in a sentence are called noun clauses. Nominal clauses can act as subject, object, predicate, appositive and other components in compound sentences. According to the above-mentioned different grammatical functions, nominal clauses are divided into subject clause, object clause, predicate clause and appositive clause. In this unit, we will review the three kinds of nominal clauses. Appositive clauses are not required to be mastered in the optional compulsory stage, so they are not involved.1. Guide the students to judge the compound sentences and determine the composition of the clauses in the sentence.2. Instruct students to try to learn grammar by generalizing grammar rules, controlling written practice, and semi-open oral output.3. Inspire the students to systematize the function and usage of noun clause1.Instruct students to try to learn grammar by generalizing grammar rules, controlling written practice, and semi-open oral output.2.Inspire the students to systematize the function and usage of noun clauseStep1: The teacher ask studetns to find out more nominal clauses from the reading passage and udnerline the nominal clauses.

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 3 Food and Culture-Reading and thinking教学设计
The discourse explores the link between food and culture from a foreign’s perspective and it records some authentic Chinese food and illustrates the cultural meaning, gerography features and historic tradition that the food reflects. It is aimed to lead students to understand and think about the connection between food and culture. While teaching, the teacher should instruct students to find out the writing order and the writer’s experieces and feelings towards Chinese food and culture.1.Guide the students to read the text, sort out the information and dig out the topic.2.Understand the cultural connotation, regional characteristics and historical tradition of Chinese cuisine3.Understand and explore the relationship between food and people's personality4.Guide the students to use the cohesive words in the text5.Lead students to accurately grasp the real meaning of the information and improve the overall understanding ability by understanding the implied meaning behind the text.1. Enable the Ss to understand the structure and the writing style of the passage well.2. Lead the Ss to understand and think further about the connection between food and geography and local character traits.Step1: Prediction before reading. Before you read, look at the title, and the picture. What do you think this article is about?keys:It is about various culture and cuisine about a place or some countries.

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 5 First Aid-Discovering useful structures教学设计
You have no excuse for not going.你没有理由不去。He was punished for not having finished his homework.他因未完成作业而受到惩罚。2.动词ing形式复合结构由物主代词或人称代词宾格、名词所有格或普通格加动词ing,即“sb./sb.'s+doing”构成。动词ing形式的复合结构实际上是给动词ing形式加了一个逻辑主语。动词ing形式的复合结构有四种形式:①形容词性物主代词+动词ing②名词所有格+动词ing③代词宾格+动词ing④名词+动词ingHer coming to help encouraged all of us.她来帮忙鼓舞了我们所有人。The baby was made awake by the door suddenly shutting.这个婴儿被突然的关门声吵醒了。Can you imagine him/Jack cooking at home?你能想象他/杰克在家做饭的样子吗?无生命名词无论是作主语还是作宾语都不能用第②种形式。Tom's winning first prize last year impressed me a lot.汤姆去年得了一等奖使我印象深刻。Do you mind my/me/Jack's/Jack leaving now?你介意我/杰克现在离开吗?Excuse me for my not coming on time.很抱歉我没能按时来。His father's being ill made him worried.他父亲病了,他很担心。We are looking forward to the singer's/the singer to give us a concert.我们盼望着这位歌手来给我们举办一场演唱会。
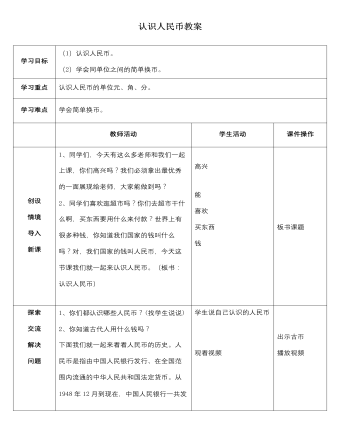
人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册认识人民币教案
教师活动创设情境导入新课 1、 同学们,今天有这么多老师和我们一起上课,你们高兴吗?我们必须拿出最优秀的一面展现给老师,大家能做到吗?2、同学们喜欢逛超市吗?你们去超市干什么啊,买东西要用什么来付款?世界上有很多种钱,你知道我们国家的钱叫什么吗?对,我们国家的钱叫人民币,今天这节课我们就一起来认识人民币。(板书:认识人民币)探索交流解决问题1、 你们都认识哪些人民币?(找学生说说)2、 你知道古代人用什么钱吗?下面我们就一起来看看人民币的历史。人民币是指由中国人民银行发行、在全国范围内流通的中华人民共和国法定货币。从1948年12月到现在,中国人民银行一共发行了五套人民币。分别是:1948年12月1日发行的第一套人民币;1955年3月1日发行的第二套人民币;1962年4月15日发行的第三套人民币;1987年4月27日发行的第四套人民币。还有1999年10月1日发行的第五套人民币也就是目前市场上流通的人民币。 请同学们仔细观察,这些钱你们都认识吗?(屏幕显示)人民币上有什么?(国徽)国徽是我们国家的标志,许多人民币上都有国徽,所以我们应该爱护它,不要故意损坏它。瞧,我们国家的人民币有这么多呢!有些是纸做的,叫纸币,(课件突出显示纸币)有的是金属做的,叫硬币。(课件突出显示硬币)2、特征辨认。师:这些人民币你们都认识吗?3、 师:那好,老师来考考你们这张人民币的面值是多少?你是怎么知道的?(同学们观察的真仔细)4、 看下面几张你都认识吗?5、 同学们学的真认真,老师中午回家要乘坐无人售票车,这种车要求自觉投币1元而不找零钱,老师只有一张10元的人民币,老师该怎么办哪?6、谁能帮老师换换钱?

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册人民币的认识教案2篇
出示例6挂图。教师试问:谁知道0.50元是几角?2.00元是几角?你是怎么知道?以元为单位小数点左边是几就是几元,右边第一位是几就是几角,右边第二位是几就是几分。1.20元是1元2角。35.90元是35元9角。(这部分知识学生知道它表示几元几角就可以了,至于1.20元是个什么数,怎么读、写不需要学生掌握)3、教学例7。(1) 课件演示例7第一小题。教师:0.5元是几角?(5角)0.80元是几角?(8角)学生回答。5角+8角是几角?(5角+8角=13角教师板书)教师问:多少角是1元?13角里面拿出10角还剩多少角?(3角)所以13角等于1元3角。教师板书:5角+8角=13角=1元3角。(2)例7第二小题(课件演示,提出问题:我买这两个气球要多少钱)学生尝试完成,然后提问:你是怎么想的?教师强调:元、角计算,只有在相同单位的情况下,才能相加。

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册人民币的简单计算教案
人民币的简单计算是在对人民币的认识后,是人民币的再进一步的认识。本节课的主要知识点主要有三个:一人民币单位间的换算、二进行简单的计算,三是知道商品价格的表示形式。同时通过这节课的学习,逐渐培养交往和社会实践能力,体会人民币在社会生活商品交换中的作用。为了达成以上的一些目标我是这样设计这节课。一、从学生经验入手直接引入商品价格,在学生回忆商品价格的表示方法中,唤醒学生的思绪,使学生觉得在所学的知识与实际生活的联系。让学生体验到数学与日常生活的密切联系。二、在操作中完成进率的换算。进率的换算在教学是一个重点也是难点,为此我在教学上通过不同的的付钱方法,深刻体会,这样的教学让说不清的关系,在操作讲解中得以内化。学生学了也不易忘记。

新人教版高中英语必修3Unit 5 The Value of Money-Discovering Useful Structures导学案
4.They were going to find someone to take part in their bet when they saw Henry walking on the street outside.[归纳]1.过去将来时的基本构成和用法过去将来时由“would+动词原形”构成,主要表示从过去某一时间来看将要发生的动作(尤其用于宾语从句中),还可以表示过去的动作习惯或倾向。Jeff knew he would be tired the next day.He promised that he would not open the letter until 2 o'clock.She said that she wouldn't do that again.2.表示过去将来时的其他表达法(1)was/were going to+动词原形:该结构有两个主要用法,一是表示过去的打算,二是表示在过去看来有迹象表明将要发生某事。I thought it was going to rain.(2)was/were to+动词原形:主要表示过去按计划或安排要做的事情。She said she was to get married next month.(3)was/were about to+动词原形:表示在过去看来即将要发生的动作,由于本身已含有“即将”的意味,所以不再与表示具体的将来时间状语连用。I was about to go to bed when the phone rang.(4)was/were+现在分词:表示在过去看来即将发生的动作,通常可用于该结构中的动词是come,go,leave,arrive,begin,start,stop,close,open,die,join,borrow,buy等瞬间动词。Jack said he was leaving tomorrow.

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册平面图形的拼组教案
朋友们都听说了我们的神奇魔力,米老鼠也来请我们帮忙了,你们愿意帮他把墙修补好吗?(幻灯11,同时请一名同学到台前来亲自动手粘一下)在我们的帮助下,米老鼠家缺了10块砖的墙就被修补好了(幻灯12)七、拼图大比赛。1、师:现在请同学们运用自己手中的所有材料,发挥你的想象,可以自己拼,也可以和组员合作拼出自己喜欢的图形,比一比,看那些同学拼得又好又快,又有创意。 2、展示学生作品。学生自己评价或者互相评价。八、欣赏品评,知识延伸 师:同学们刚才拼的图形非常漂亮,老师很喜欢。生活中有许多地方都需要优美的图形的装饰,同学们也可以是一位小小设计师,设计出美丽的图案,装点生活,美化环境。(欣赏生活中的优秀装饰作品) 师:通过刚才的欣赏,你有什么想法?

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册小小商店教案2篇
3、同学们,你们看今天老师带来了什么?(出示一个学生喜欢的玩具)这是昨天老师去商店时买的,猜猜看,这个需要多少钱?(学生猜,教师可提示,最后得出正确标价)今天我们也来开个小小商店玩一玩买卖商品的游戏,想玩吗?4、选营业员及经理。我觉得当营业员最重要的是精通业务,计算能力强。谁想来当?(等学生举手后,教师选出4人。)考虑到我们呆会儿买的人会比较多,每个柜台一个营业员忙不过来,我还准备再选4名商店经理,做好以下几项工作:1)做好接待服务工作,顾客有困难能主动帮助。2)做好买卖过程中的组织工作,让大家有秩序地买商品。3)当营业员计算碰到困难时,两人能商量着解决。觉得自己能做到以上三点的同学可举手参加竞选。(学生举手后,选出4名经理)

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册20以内的退位减法教案2篇
一、揭题:小朋友们,今天我们一起来做练习。二、练习:1、第8题:这是一道计算题。(1)明确要求:看谁算得又对又快。(2)学生独立完成。(3)订正答案。(4)有错的学生,说一说计算顺序是怎样的,每一步的计算结果是多少?2、第9题:这是一道用数学的题。(1)看图,同位两个互相说说图意,并提出数学问题。(2)根据问题列算式解答。(3)订正答案。3、第10题:比一比。(1)明确要求,看谁先夺得红旗。(2)各小组派代表参加比赛。(3)对算得又对又快的学生提出表扬,并奖励给一个小标志。(4)再加入几组比赛题,尽量让学生多参与。4、第11题:这是一道用数学的题。(1)看图,说图意,提出数学问题。(2)列算式解答,指名板演订正。(3)说一说为什么用加法计算?5、思考题:小组讨论完成。一共12人,每两人之间插入一个女生,一共能插入11人。

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册100以内的加法和减法(一)教案
一、谈话引入,激发学生学习兴趣师:六一快到了,很多小朋友都想了很多的方式来庆祝,有的小朋友想去公园,有的小朋友想用自己攒的零花钱去买玩具呢,我们也和他们一起去看看吧!(电脑出示玩具店的货架和玩具的标价。)二、自主探索,提出问题。1、仔细看图,提出问题师:看货架上都有哪些玩具?你喜欢什么玩具?你从图上知道了哪些信息?(观察后指名回答。)课件出示:两个小朋友的对话师:货架下的两个小朋友在说什么?你知道了什么信息?(指明生说出题意)师:怎样才知道左边的小朋友买大象玩具后还剩多少元?右边的小朋友还差多少元呢?(用减法算)师:你知道这么列式吗?(师根据生回答板书算式)师:大家会算上面的算式吗?先在小组里摆一摆,算一算。2、分组操作,形成思维。学生摆小棒,教师巡回指导学生操作。3、信息反馈,抽象算法。师:大家摆出了上面两道题的得数吗?谁来说一说是怎样摆的?

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册两位数加一位数和整十数教案
二、新授:1、出示屏幕,教师给小朋友发新书了。你可以提出哪些数学问题?(引导学生认真观察情景图)(数学书有多少本?语文书有多少本?一包数学书和一包语文书共有多少本?零星的语文书和数学书共有多少本?)2、学生独立从图上寻找解决问题所需要的数据和信息。板书:35+3 30+8 35+30 8+3请你找一找,哪几个算式已经学过了?得数是多少?(30+8=38,8+3=11)[那么剩下的两道道题35+3 35+30就是我们今天要学的内容:两位数加一位数和整十数(引导学生得出课题并板书)。请同学们想想35+3 35+30得多少呢?首先请同学们看第一题35+3我们可以用什么方法来计算呢?3、四人小组讨论交流各种计算方法生:接着数,摆小棒······A.动手操作:用小棒摆:先摆3捆5根加上3根得到8根小棒,再和3捆小棒合起来是38。出示3捆5根加上3根得到38。(生自己动手操作并请摆得好的学生演示)不用小棒也可以直接算:先把个位上的5加上3得8,再加30得38B.观察算式,掌握口算的方法

