-
高教版中职数学基础模块下册:6.1《数列的概念》教案设计
【教学目标】1. 理解数列的通项公式的意义,能根据通项公式写出数列的任意一项,以及根据其前几项写出它的一个通项公式.2. 了解数列的递推公式,会根据数列的递推公式写出前几项.3.培养学生积极参与、大胆探索的精神,培养学生的观察、分析、归纳的能力.教学重点 数列的通项公式及其应用.教学难点 根据数列的前几项写出满足条件的数列的一个通项公式.教学方法 本节课主要采用例题解决法.通过列举实例,进一步研究数列的项与序号之间的关系.通过三类题目,使学生深刻理解数列通项公式的意义,为以后学习等差数列与等比数列打下基础.【教学过程】 环节教学内容师生互动设计意图导 入⒈数列的定义 按一定次序排列的一列数叫做数列. 注意:(1)数列中的数是按一定次序排列的; (2)同一个数在数列中可以重复出现. 2. 数列的一般形式 数列a1,a2,a3,…,an,…,可记作{ an }. 3. 数列的通项公式: 如果数列{ an }的第n项an与n之间的关系可以用一个公式来表示,那么这个公式就叫做这个数列的通项公式. 教师引导学生复习. 为学生进一步理解通项公式,应用通项公式解决实际问题做好准备.
高教版中职数学基础模块下册:6.2《等差数列》教学设计
系(部)医药授课教师戚文撷授课班级11(5),11(6)班授课类型新授课授课时数2课时授课周数第一周授课日期2012.2.15授课地点 教室课题第六章数列分课题§6.2 等差数列教学目标1. 理解等差数列的概念,掌握等差数列的通项公式;掌握等差中项的概念. 2. 逐步灵活应用等差数列的概念和通项公式解决问题. 3.等差数列的前N项之和 . 4.培养学生分析、比较、归纳的逻辑思维能力. . 2. 3.教学重点等差数列的概念及其通项公式. 教学难点等差数列通项公式的灵活运用. 教学方法情境教学法、自主探究式教学方法教学器材及设备黑板、粉笔复习提问提问内容姓名成绩1.数列的定义? 答: 2. 数列的通项公式? 答: 板书设计 §6.2.1等差数列的概念 1. 1.等差数列的定义 公差:d 2.常数列 3.等差数列的通项公式 an=a1+(n-1)d. 等差数列的前n 项和公式: 例题 练习作业布置习题第1,2题.课后小结本节课主要采用自主探究式教学方法.充分利用现实情景,尽可能地增加教学过程的趣味性、实践性.我再整个教学中强调学生的主动参与,让学生自己去分析、探索,在探索过程中研究和领悟得出的结论,从而达到使学生既获得知识又发展智能的目的.
高教版中职数学基础模块下册:6.3《等比数列》优秀教案设计
授课 日期 班级16高造价 课题: §6.3等比数列 教学目的要求: 1.理解等比数列的概念,能根据定义判断或证明一个数列是等比数列;2.探索并掌握等比数列的通项公式; 3.掌握等比数列前 n 项和公式及推导过程,能用公式求相关参数; 教学重点、难点:运用等比数列的通项公式求相关参数 授课方法: 任务驱动法 小组合作学习法 教学参考及教具(含多媒体教学设备): 《单招教学大纲》 授课执行情况及分析: 板书设计或授课提纲 §6.3等比数列 1.等比数列的概念 (学生板书区) 2. 等比数列的通项公式 3.等比数列的求和公式

高教版中职数学基础模块下册:8.3《两条直线的位置关系》教案设计
教 学 过 程教师 行为学生 行为教学 意图 *揭示课题 8.3 两条直线的位置关系(二) *创设情境 兴趣导入 【问题】 平面内两条既不重合又不平行的直线肯定相交.如何求交点的坐标呢? 图8-12 介绍 质疑 引导 分析 了解 思考 启发 学生思考 *动脑思考 探索新知 如图8-12所示,两条相交直线的交点,既在上,又在上.所以的坐标是两条直线的方程的公共解.因此解两条直线的方程所组成的方程组,就可以得到两条直线交点的坐标. 观察图8-13,直线、相交于点P,如果不研究终边相同的角,共形成四个正角,分别为、、、,其中与,与为对顶角,而且. 图8-13 我们把两条直线相交所成的最小正角叫做这两条直线的夹角,记作. 规定,当两条直线平行或重合时,两条直线的夹角为零角,因此,两条直线夹角的取值范围为. 显然,在图8-13中,(或)是直线、的夹角,即. 当直线与直线的夹角为直角时称直线与直线垂直,记做.观察图8-14,显然,平行于轴的直线与平行于轴的直线垂直,即斜率为零的直线与斜率不存在的直线垂直. 图8-14 讲解 说明 讲解 说明 引领 分析 仔细 分析 讲解 关键 词语 思考 思考 理解 思考 理解 记忆 带领 学生 分析 带领 学生 分析 引导 式启 发学 生得 出结 果
【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:1.3《正弦定理与余弦定理》教案设计
教 学 过 程教师 行为学生 行为教学 意图 *揭示课题 1.3正弦定理与余弦定理. *创设情境 兴趣导入 在实际问题中,经常需要计算高度、长度、距离和角的大小,这类问题中有许多与三角形有关,可以归结为解三角形问题. 介绍 播放 课件 质疑 了解 观看 课件 思考 学生自然的走向知识点*巩固知识 典型例题 例6 一艘船以每小时36海里的速度向正北方向航行(如图1-9).在A处观察到灯塔C在船的北偏东方向,小时后船行驶到B处,此时灯塔C在船的北偏东方向,求B处和灯塔C的距离(精确到0.1海里). 图1-9 A 解因为∠NBC=,A=,所以.由题意知 (海里). 由正弦定理得 (海里). 答:B处离灯塔约为海里. 例7 修筑道路需挖掘隧道,在山的两侧是隧道口A和(图1-10),在平地上选择适合测量的点C,如果,m,m,试计算隧道AB的长度(精确到m). 图1-10 解 在ABC中,由余弦定理知 =. 所以 m. 答:隧道AB的长度约为409m. 例8 三个力作用于一点O(如图1-11)并且处于平衡状态,已知的大小分别为100N,120N,的夹角是60°,求F的大小(精确到1N)和方向. 图1-11 解 由向量加法的平行四边形法则知,向量表示F1,F2的合力F合,由力的平衡原理知,F应在的反向延长线上,且大小与F合相等. 在△OAC中,∠OAC=180°60°=120°,OA=100, AC=OB=120,由余弦定理得 OC= = ≈191(N). 在△AOC中,由正弦定理,得 sin∠AOC=≈0.5441, 所以∠AOC≈33°,F与F1间的夹角是180°–33°=147°. 答:F约为191N,F与F合的方向相反,且与F1的夹角约为147°. 引领 讲解 说明 引领 观察 思考 主动 求解 观察 通过 例题 进一 步领 会 注意 观察 学生 是否 理解 知识 点
【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:1.2《正弦型函数》教学设计
教 学 过 程教师 行为学生 行为教学 意图时间 *揭示课题 1.2正弦型函数. *创设情境 兴趣导入 与正弦函数图像的做法类似,可以用“五点法”作出正弦型函数的图像.正弦型函数的图像叫做正弦型曲线. 介绍 播放 课件 质疑 了解 观看 课件 思考 学生自然的走向知识点 0 5*巩固知识 典型例题 例3 作出函数在一个周期内的简图. 分析 函数与函数的周期都是,最大值都是2,最小值都是-2. 解 为求出图像上五个关键点的横坐标,分别令,,,,,求出对应的值与函数的值,列表1-1如下: 表 001000200 以表中每组的值为坐标,描出对应五个关键点(,0)、(,2)、(,0)、(,?2)、(,0).用光滑的曲线联结各点,得到函数在一个周期内的图像(如图). 图 引领 讲解 说明 引领 观察 思考 主动 求解 观察 通过 例题 进一 步领 会 注意 观察 学生 是否 理解 知识 点 15
【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:1.3《正弦定理与余弦定理》教学设计
教 学 过 程教师 行为学生 行为教学 意图时间 *揭示课题 1.3正弦定理与余弦定理. *创设情境 兴趣导入 在实际问题中,经常需要计算高度、长度、距离和角的大小,这类问题中有许多与三角形有关,可以归结为解三角形问题,经常需要应用正弦定理或余弦定理. 介绍 播放 课件 了解 观看 课件 学生自然的走向知识点 0 5*巩固知识 典型例题 例6一艘船以每小时36海里的速度向正北方向航行(如图1-14).在A处观察灯塔C在船的北偏东30°,0.5小时后船行驶到B处,再观察灯塔C在船的北偏东45°,求B处和灯塔C的距离(精确到0.1海里). 解 因为∠NBC=45°,A=30°,所以C=15°, AB = 36×0.5 = 18 (海里). 由正弦定理得 答:B处离灯塔约为34.8海里. 例7 修筑道路需挖掘隧道,在山的两侧是隧道口A和B(图1-15),在平地上选择适合测量的点C,如果C=60°,AB = 350m,BC = 450m,试计算隧道AB的长度(精确到1m). 解 在△ABC中,由余弦定理知 =167500. 所以AB≈409m. 答:隧道AB的长度约为409m. 图1-15 引领 讲解 说明 引领 观察 思考 主动 求解 观察 通过 例题 进一 步领 会 注意 观察 学生 是否 理解 知识 点 40
【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:3.1《排列与组合》优秀教学设计
教 学 过 程教师 行为学生 行为教学 意图时间 *揭示课题 3.1 排列与组合. *创设情境 兴趣导入 基础模块中,曾经学习了两个计数原理.大家知道: (1)如果完成一件事,有N类方式.第一类方式有k1种方法,第二类方式有k2种方法,……,第n类方式有kn种方法,那么完成这件事的方法共有 = + +…+(种). (3.1) (2)如果完成一件事,需要分成N个步骤.完成第1个步骤有k1种方法,完成第2个步骤有k2种方法,……,完成第n个步骤有kn种方法,并且只有这n个步骤都完成后,这件事才能完成,那么完成这件事的方法共有 = · ·…·(种). (3.2) 下面看一个问题: 在北京、重庆、上海3个民航站之间的直达航线,需要准备多少种不同的机票? 这个问题就是从北京、重庆、上海3个民航站中,每次取出2个站,按照起点在前,终点在后的顺序排列,求不同的排列方法的总数. 首先确定机票的起点,从3个民航站中任意选取1个,有3种不同的方法;然后确定机票的终点,从剩余的2个民航站中任意选取1个,有2种不同的方法.根据分步计数原理,共有3×2=6种不同的方法,即需要准备6种不同的飞机票: 北京→重庆,北京→上海,重庆→北京,重庆→上海,上海→北京,上海→重庆. 介绍 播放 课件 质疑 了解 观看 课件 思考 引导 启发学生得出结果 0 15*动脑思考 探索新知 我们将被取的对象(如上面问题中的民航站)叫做元素,上面的问题就是:从3个不同元素中,任取2个,按照一定的顺序排成一列,可以得到多少种不同的排列. 一般地,从n个不同元素中,任取m (m≤n)个元素,按照一定的顺序排成一列,叫做从n个不同元素中取出m个元素的一个排列,时叫做选排列,时叫做全排列. 总结 归纳 分析 关键 词语 思考 理解 记忆 引导学生发现解决问题方法 20

【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:3.2《二项式定理》教学设计
一、定义: ,这一公式表示的定理叫做二项式定理,其中公式右边的多项式叫做的二项展开式;上述二项展开式中各项的系数 叫做二项式系数,第项叫做二项展开式的通项,用表示;叫做二项展开式的通项公式.二、二项展开式的特点与功能1. 二项展开式的特点项数:二项展开式共(二项式的指数+1)项;指数:二项展开式各项的第一字母依次降幂(其幂指数等于相应二项式系数的下标与上标的差),第二字母依次升幂(其幂指数等于二项式系数的上标),并且每一项中两个字母的系数之和均等于二项式的指数;系数:各项的二项式系数下标等于二项式指数;上标等于该项的项数减去1(或等于第二字母的幂指数;2. 二项展开式的功能注意到二项展开式的各项均含有不同的组合数,若赋予a,b不同的取值,则二项式展开式演变成一个组合恒等式.因此,揭示二项式定理的恒等式为组合恒等式的“母函数”,它是解决组合多项式问题的原始依据.又注意到在的二项展开式中,若将各项中组合数以外的因子视为这一组合数的系数,则易见展开式中各组合数的系数依次成等比数列.因此,解决组合数的系数依次成等比数列的求值或证明问题,二项式公式也是不可或缺的理论依据.
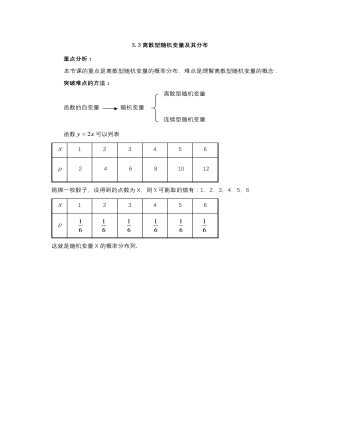
【高教版】中职数学拓展模块:3.3《离散型随机变量及其分布》教学设计
重点分析:本节课的重点是离散型随机变量的概率分布,难点是理解离散型随机变量的概念. 离散型随机变量 突破难点的方法: 函数的自变量 随机变量 连续型随机变量 函数可以列表 X123456p 2 4 6 8 10 12
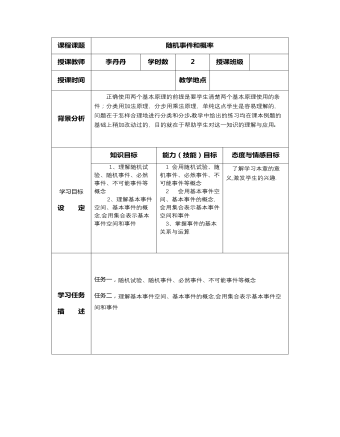
高教版中职数学基础模块下册:10.2《概率》教学设计
课程课题随机事件和概率授课教师李丹丹学时数2授课班级 授课时间 教学地点 背景分析正确使用两个基本原理的前提是要学生清楚两个基本原理使用的条件;分类用加法原理,分步用乘法原理,单纯这点学生是容易理解的,问题在于怎样合理地进行分类和分步教学中给出的练习均在课本例题的基础上稍加改动过的,目的就在于帮助学生对这一知识的理解与应用 学习目标 设 定知识目标能力(技能)目标态度与情感目标1、理解随机试验、随机事件、必然事件、不可能事件等概念 2、理解基本事件空间、基本事件的概念,会用集合表示基本事件空间和事件 1 会用随机试验、随机事件、必然事件、不可能事件等概念 2 会用基本事件空间、基本事件的概念,会用集合表示基本事件空间和事件 3、掌握事件的基本关系与运算 了解学习本章的意义,激发学生的兴趣. 学习任务 描 述 任务一,随机试验、随机事件、必然事件、不可能事件等概念 任务二,理解基本事件空间、基本事件的概念,会用集合表示基本事件空间和事件

人教版新课标小学数学五年级下册设计镶嵌图案教案
师:同学们,在四年级的时候,我们已经了解了图形的密铺,请你说一说,什么是图形的密铺?(没有重叠、没有空隙地铺在平面上,就是密铺。)师:图形的密铺又可以叫做镶嵌,以上四个图片,都是由哪些基本图形密铺(镶嵌)而成的呢?(请学生边指边说。)师:还有哪些图形也可以镶嵌?(学生可能回答:三角形,平行四边形,梯形,菱形,正六边形,……)师:今天就请你发挥一下想象力,设计一些与众不同的镶嵌图形。[设计意图说明:学生在四年级已经初步了解了图形的密铺(镶嵌)现象,四幅图片是四年级下册教材《三角形》单元中《密铺》内容中的原图。本单元在此基础上,通过数学游戏拓展镶嵌图形的范围,让学生用图形变换设计镶嵌图案,进一步感受图形变换带来的美感以及在生活中的应用。]二、新授探究一:利用平移变换设计镶嵌图形

人教版新课标小学数学一年级下册人民币的简单计算教案
人民币的简单计算是在对人民币的认识后,是人民币的再进一步的认识。本节课的主要知识点主要有三个:一人民币单位间的换算、二进行简单的计算,三是知道商品价格的表示形式。同时通过这节课的学习,逐渐培养交往和社会实践能力,体会人民币在社会生活商品交换中的作用。为了达成以上的一些目标我是这样设计这节课。一、从学生经验入手直接引入商品价格,在学生回忆商品价格的表示方法中,唤醒学生的思绪,使学生觉得在所学的知识与实际生活的联系。让学生体验到数学与日常生活的密切联系。二、在操作中完成进率的换算。进率的换算在教学是一个重点也是难点,为此我在教学上通过不同的的付钱方法,深刻体会,这样的教学让说不清的关系,在操作讲解中得以内化。学生学了也不易忘记。

人教版新课标小学数学六年级下册扇形统计图教案
2 根据下面4幅,你能判断出哪个学校的女生人数最多吗?(1) 如果甲校的学生总人数900人,那么甲校的女生有多少人?(2) 如果丙校男生与甲校的同样多,那么丙校学生总人数有多少人?(3) 如果乙校的学生总人数与丙校的同样多,那么乙校男生有多少人?(4) 如果丁校的男生与乙校的同样多,那么乙校的女生有多少人?3 出示课件《中国人口占世界的百分比》和《中国国土面积占世界的百分比》统计图和有关的数据。(1)中国人口约13亿 (2)中国国土面积约960万平方千米(请同学认真观察统计图和有关的数据,请你说说获得了哪些信息?并提出我们能够解决的问题。要求:先在小组交流,然后派代表提出问题,并指定他组回答,其他同学当评委;如果回答正确,由的同学提问题,否则,由提问题的同学继续提问。同组成员可帮助。)还有什么想法?3 出示西山村果园各种果树种植面积情况,要求学生根据给出的数据制成扇形统计图。

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Discovering useful structures教学设计
The grammatical structure of this unit is predicative clause. Like object clause and subject clause, predicative clause is one of Nominal Clauses. The leading words of predicative clauses are that, what, how, what, where, as if, because, etc.The design of teaching activities aims to guide students to perceive the structural features of predicative clauses and think about their ideographic functions. Beyond that, students should be guided to use this grammar in the context apporpriately and flexibly.1. Enable the Ss to master the usage of the predicative clauses in this unit.2. Enable the Ss to use the predicative patterns flexibly.3. Train the Ss to apply some skills by doing the relevant exercises.1.Guide students to perceive the structural features of predicative clauses and think about their ideographic functions.2.Strengthen students' ability of using predicative clauses in context, but also cultivate their ability of text analysis and logical reasoning competence.Step1: Underline all the examples in the reading passage, where noun clauses are used as the predicative. Then state their meaning and functions.1) One theory was that bad air caused the disease.2) Another theory was that cholera was caused by an infection from germs in food or water.3) The truth was that the water from the Broad Street had been infected by waste.Sum up the rules of grammar:1. 以上黑体部分在句中作表语。2. 句1、2、3中的that在从句中不作成分,只起连接作用。 Step2: Review the basic components of predicative clauses1.Definition

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 4 Journey Across a Vast Land教学设计
当孩子们由父母陪同时,他们才被允许进入这个运动场。3.过去分词(短语)作状语时的几种特殊情况(1)过去分词(短语)在句中作时间、条件、原因、让步状语时,相当于对应的时间、条件、原因及让步状语从句。Seen from the top of the mountain (=When it is seen from the top of the mountain), the whole town looks more beautiful.从山顶上看,整个城市看起来更美了。Given ten more minutes (=If we are given ten more minutes), we will finish the work perfectly.如果多给十分钟,我们会完美地完成这项工作。Greatly touched by his words (=Because she was greatly touched by his words), she was full of tears.由于被他的话深深地感动,她满眼泪花。Warned of the storm (=Though they were warned of the storm), the farmers were still working on the farm.尽管被警告了风暴的到来,但农民们仍在农场干活。(2)过去分词(短语)在句中作伴随、方式等状语时,可改为句子的并列谓语或改为并列分句。The teacher came into the room, followed by two students (=and was followed by two students).后面跟着两个学生,老师走进了房间。He spent the whole afternoon, accompanied by his mom(=and was accompanied by his mom).他由母亲陪着度过了一整个下午。

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Learning about Language教学设计
Step 7: complete the discourse according to the grammar rules.Cholera used to be one of the most 1.__________ (fear) diseases in the world. In the early 19th century, _2_________ an outbreak of cholera hit Europe, millions of people died. But neither its cause, 3__________ its cure was understood. A British doctor, John Snow, wanted to solve the problem and he knew that cholera would not be controlled _4_________ its cause was found. In general, there were two contradictory theories 5 __________ explained how cholera spread. The first suggested that bad air caused the disease. The second was that cholera was caused by an _6_________(infect) from germs in food or water. John Snow thought that the second theory was correct but he needed proof. So when another outbreak of cholera hit London in 1854, he began to investigate. Later, with all the evidence he _7_________ (gather), John Snow was able to announce that the pump water carried cholera germs. Therefore, he had the handle of the pump _8_________ (remove) so that it couldn't be used. Through his intervention,the disease was stopped in its tracks. What is more, John Snow found that some companies sold water from the River Thames that __9__________________ (pollute) by raw waste. The people who drank this water were much more likely _10_________ (get) cholera than those who drank pure or boiled water. Through John Snow's efforts, the _11_________ (threaten) of cholera around the world saw a substantial increase. Keys: 1.feared 2.when 3. nor 4.unless 5.that/which 6.infection 7.had gathered 8.removed 9.was polluted 10.to get 11. threat

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Reading and thinking教学设计
Step 5: After learning the text, discuss with your peers about the following questions:1.John Snow believed Idea 2 was right. How did he finally prove it?2. Do you think John Snow would have solved this problem without the map?3. Cholera is a 19th century disease. What disease do you think is similar to cholera today?SARS and Covid-19 because they are both deadly and fatally infectious, have an unknown cause and need serious public health care to solve them urgently.keys:1. John Snow finally proved his idea because he found an outbreak that was clearly related to cholera, collected information and was able to tie cases outside the area to the polluted water.2. No. The map helped John Snow organize his ideas. He was able to identify those households that had had many deaths and check their water-drinking habits. He identified those houses that had had no deaths and surveyed their drinking habits. The evidence clearly pointed to the polluted water being the cause.3. SARS and Covid-19 because they are both deadly and fatally infectious, have an unknown cause and need serious public health care to solve them urgently.Step 6: Consolidate what you have learned by filling in the blanks:John Snow was a well-known _1___ in London in the _2__ century. He wanted to find the _3_____ of cholera in order to help people ___4_____ it. In 1854 when a cholera __5__ London, he began to gather information. He ___6__ on a map ___7___ all the dead people had lived and he found that many people who had ___8____ (drink) the dirty water from the __9____ died. So he decided that the polluted water ___10____ cholera. He suggested that the ___11__ of all water supplies should be _12______ and new methods of dealing with ____13___ water be found. Finally, “King Cholera” was __14_____.Keys: 1. doctor 2. 19th 3.cause 4.infected with 5.hit 6.marked 7.where 8.drunk 9.pump 10.carried 11.source 12.examined 13.polluted 14.defeatedHomework: Retell the text after class and preview its language points

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 1 Science and Scientists-Using langauge教学设计
This happens because the dish soap molecules have a strong negative charge, and the milk molecules have a strong positive charge. Like magnets, these molecules are attracted to each other, and so they appear to move around on the plate, taking the food coloring with them, making it look like the colors are quickly moving to escape from the soap.Listening text:? Judy: Oh, I'm so sorry that you were ill and couldn't come with us on our field trip. How are you feeling now? Better?? Bill: Much better, thanks. But how was it?? Judy: Wonderful! I especially liked an area of the museum called Light Games.it was really cool. They had a hall of mirrors where I could see myself reflected thousands of times!? Bill: A hall of mirrors can be a lot of fun. What else did they have?? Judy: Well, they had an experiment where we looked at a blue screen for a while, and then suddenly we could see tiny bright lights moving around on it. You'll never guess what those bright lights were!? Bill: Come on, tell me!? Judy: They were our own blood cells. For some reason, our eyes play tricks on us when we look at a blue screen, and we can see our own blood cells moving around like little lights! But there was another thing I liked better. I stood in front of a white light, and it cast different shadows of me in every color of the rainbow!? Bill: Oh, I wish I had been there. Tell me more!? Judy: Well, they had another area for sound. They had a giant piano keyboard that you could use your feet to play. But then, instead of playing the sounds of a piano, it played the voices of classical singers! Then they had a giant dish, and when you spoke into it, it reflected the sound back and made it louder. You could use it to speak in a whisper to someone 17 meters away.? Bill: It all sounds so cool. I wish I could have gone with you? Judy: I know, but we can go together this weekend. I'd love to go there again!? Bill: That sounds like a great idea!

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 2 Bridging Cultures-Discovering useful structures教学设计
The grammar of this unit is designed to review noun clauses. Sentences that use nouns in a sentence are called noun clauses. Nominal clauses can act as subject, object, predicate, appositive and other components in compound sentences. According to the above-mentioned different grammatical functions, nominal clauses are divided into subject clause, object clause, predicate clause and appositive clause. In this unit, we will review the three kinds of nominal clauses. Appositive clauses are not required to be mastered in the optional compulsory stage, so they are not involved.1. Guide the students to judge the compound sentences and determine the composition of the clauses in the sentence.2. Instruct students to try to learn grammar by generalizing grammar rules, controlling written practice, and semi-open oral output.3. Inspire the students to systematize the function and usage of noun clause1.Instruct students to try to learn grammar by generalizing grammar rules, controlling written practice, and semi-open oral output.2.Inspire the students to systematize the function and usage of noun clauseStep1: The teacher ask studetns to find out more nominal clauses from the reading passage and udnerline the nominal clauses.

